The inverted cup and handle pattern is a bearish continuation pattern that typically indicates a potential decline in prices after a period of consolidation. This pattern is the inverse of the bullish cup and handle pattern and is used by traders to identify selling opportunities. This is one of the stock market patterns.
Key characteristics of an inverted cup and handle pattern
Inverted cup formation
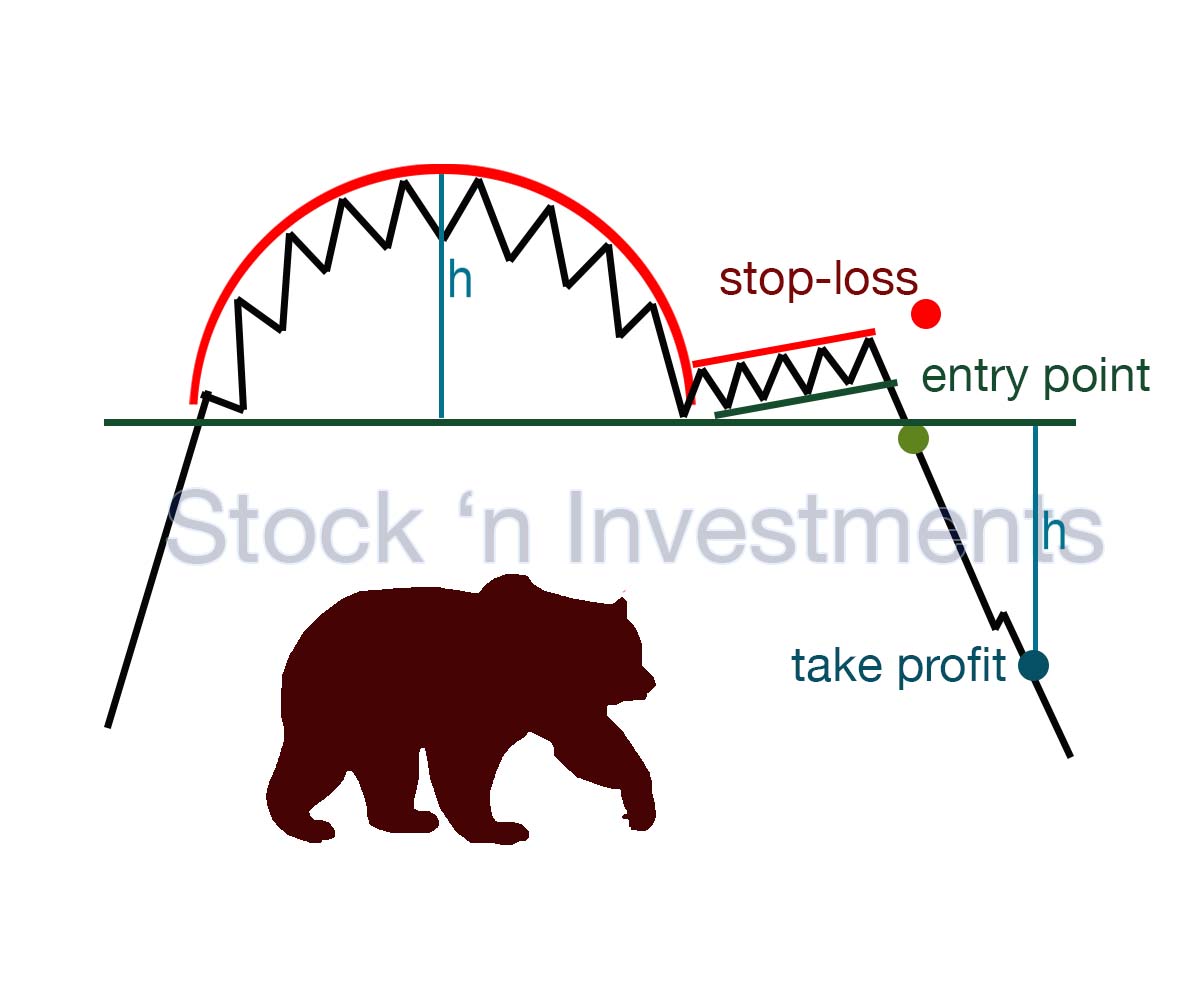
The inverted cup is shaped like an upside-down “U” or an arch. It forms after an upward trend, indicating a potential reversal.
Handle formation
After the reversal of the cup, the price consolidates, forming a small upward retracement that resembles the handle of the cup. This handle is usually shorter than the cup.
Breakout of the inverse cup and handle pattern
The breakout occurs when the price decisively breaks below this support level and stays below it. To confirm the breakout, it is important to look for an increase in trading volume, indicating the strength of the move.
Volume
In the inverted cup and handle pattern, volume plays a crucial role in confirming the pattern and its breakout.
Cup formation. Volume generally decreases as the price forms the inverted cup. This indicates weakening momentum as the price rises to form the peak of the cup and then begins to decline.
Handle formation. Volume often remains lower during the formation of the handle. This consolidation phase reflects reduced trading activity as the market prepares for the next move.
Breakout. A significant increase in volume is expected during the breakout below the support level of the handle. This surge in volume confirms the strength and validity of the breakout, indicating strong selling pressure and higher likelihood of continued downward movement.
Analysis of the inverted cup and handle pattern
Identify the pattern. Look for an inverse cup shape followed by a handle. The cup should form after a significant uptrend and the handle should be a small upward retracement.
Wait for the breakout. Monitor the price action for a breakdown below the support level at the bottom of the inverted cup. This breakdown signals a potential continuation of the bearish trend.
Confirm the breakdown. Ensure that the breakdown is accompanied by an increase in trading volume. A volume spike confirms the strength and validity of the breakdown.
Entry point. Enter a short position when the price breaks below the support level and the breakdown is confirmed by increased volume. It’s often prudent to wait for a candle to close below the support level before entering the trade.
Stop-loss placement. Place a stop-loss order above the handle or recent swing high to protect against false breakouts and limit potential losses.
Profit target. Determine a profit target by measuring the height of the cup (the distance from the bottom of the cup to the top) and projecting this distance downward from the breakdown point. This projection gives an estimated target for the price movement.
How to determine the entry point in the inverted cup and handle pattern?
First, observe the formation of the “cup,” where the asset’s price declines, forming a concave shape. After the cup is formed, the price may build the “handle” by moving sideways or slightly upward. This may involve smaller price fluctuations or consolidation. The entry point can be identified when the price breaks below the support of the “handle” and holds below this lower boundary. This indicates the beginning of a further price decline.
To confirm the entry point, it is important to watch the trading volume. An increase in volume during the breakout below the support of the “handle” confirms the strength of the move and can enhance confidence in the entry point.
What should I do when a breakout occurs?
During a breakout, you have two options: sell the asset or open a short position.
How to determine the exit point in the inverted cup and handle pattern?
To determine the exit point in the inverse cup and handle pattern, traders typically look for signs of a reversal or exhaustion in the price movement.
First, identify a resistance level near the peak of the pattern’s cup formation. This level may act as a barrier preventing further upward movement. If the price breaks above the resistance level, it could signal a bullish breakout and an opportunity to exit the position. Watch for increased trading volume during the breakout.
Calculate a price target by measuring the height of the cup and adding it to the breakout point. This can provide a potential target for exiting the position.
Use technical indicators such as moving averages, RSI, or MACD to identify overbought conditions or bearish divergence, signaling a potential reversal. Implement a trailing stop-loss strategy to protect profits while allowing for potential further upside if the price continues to rise.
What mistakes can occur when trading the reverse cup and handle pattern?
False signals. Sometimes the formation of the inverted cup and handle pattern can be unpredictable, and the price may move in the opposite direction of what was expected.
Unconfirmed breakout. Breakouts may occur without confirmation by significant trading volume, leading to false signals.
Delay in breakout. The breakout may be delayed or occur earlier than expected, resulting in losses or missed opportunities.
Unexpected factors. Unexpected market events or changes in fundamental factors can influence price movement, even if the pattern looks promising.
Careless risk management. Inadequate use of stop-loss orders or improper placement of profit targets can lead to significant losses.
How to determine the risk and potential reward when trading the inverted cup and handle pattern?
Identify entry and exit points. Define the entry point (typically at the breakout above the handle’s resistance) and the exit point (often set at the pattern’s projected target level).
Calculate stop-loss level. Determine the point at which you would exit the trade if the price moves against your position. This is often set just below the handle’s support level.
Calculate reward-to-risk ratio. Estimate the potential reward by measuring the distance from the entry point to the target level. Then, divide this by the distance from the entry point to the stop-loss level. This gives you the reward-to-risk ratio.
Assess risk tolerance. Consider your risk tolerance and adjust your position size accordingly. Ensure that the potential reward justifies the risk taken.
Monitor trade. Keep an eye on the trade as it progresses and be prepared to adjust your stop-loss or take-profit levels if necessary.
What technical indicators are useful to use with the inverse cup and handle pattern?
Volume. Look for an increase in trading volume during the breakout from the handle, confirming the validity of the pattern.
Moving Averages. Monitor moving averages, such as the 50-period or 200-period moving averages, for potential support or resistance levels that align with the inverted cup and handle pattern.
Relative Strength Index (RSI). Use the RSI to identify overbought or oversold conditions, which can help confirm the strength of the breakout.
MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence). The MACD can provide signals of bullish or bearish momentum, supporting your decision to enter or exit a trade.
Fibonacci Retracement Levels. Apply Fibonacci retracement levels to the price action preceding the pattern formation to identify potential support or resistance levels.
Bollinger Bands. Bollinger Bands can help identify volatility and potential breakout points, especially when the price consolidates within the handle portion of the pattern.
Conclusion
The inverted cup and handle pattern is an important technical formation that can indicate a possible trend reversal. It occurs when prices initially decline, forming the “inverted cup,” and then recover, forming the “handle.” A breakout above the resistance level on the handle can be an indicator of further price appreciation, while a breakout to the downside can confirm the strengthening downtrend. To trade this pattern successfully, it’s important to combine it with other technical indicators and consider fundamental factors. Reliable risk and reward calculations can help ensure successful trading within the context of this formation.
Pingback: Head and Shoulders Chart Pattern: Entry and Exit Points - Stock 'n Investments
Pingback: Stock Market Patterns, 12 options Stock 'n Investments